The Secret Behind Exponential Business Models!
Why do most businesses grow relatively linearly? What is the secret behind the companies that seem to have perfected the formula to grow exponentially? While team experience and owning the resources needed for execution are important, the secret to exponential expansion lies in the business model's elements.
Albert Einstein famously said that “compound interest is the most powerful law in the universe”. The simple explanation offered by Ben Franklin is that “money makes money. And the money that money makes, makes money.” Understanding this value of exponentiality is a powerful tool in finding long-lasting success, but as an entrepreneur or investor, how can you identify or even design business models that reflect an exponential nature?
After spending the last two decades analyzing and building high-growth software companies, we have recognized some business model patterns of exponentiality, which we use here at New Normal Group to evaluate, design and grow exponential companies.
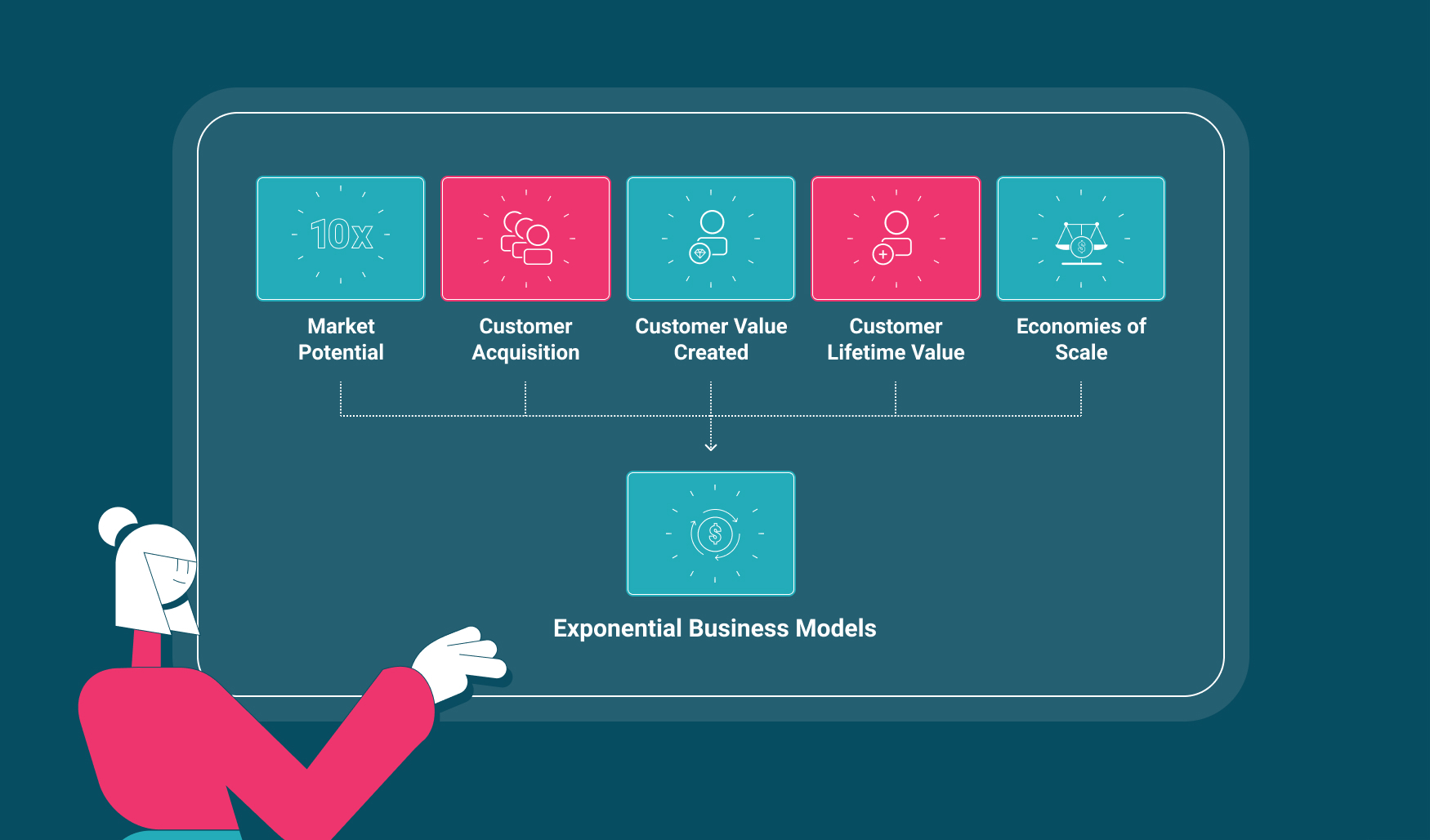
By systemizing these patterns into five different parts, we identify the building blocks of exponential business models.
We focus on the following main parts of a business model as driver of exponentially:
- Part 1: Market Potential
- Part 2: Customer Value Created
- Part 3: Customer Acquisition
- Part 4: Customer Lifetime Value
- Part 5: Economies of Scale
When several of these factors work together, we can expect to experience true exponentiality. One that follows the power laws of nature, resulting in exponential growth.
Let us dig deeper into each of these five parts and define the elements of exponentiality in a business model:
An exponential business model prerequisite is having room to grow, meaning you have to solve a large enough problem that a large number of people are willing to pay for. This is a result of the number of potential customers and their willingness to pay for such a product or service you deliver.
This implies that if you can solve a problem for many people, then you have the opportunity to see highly exponential growth, even if the price of the product is low. Alternatively, if your solution services fewer customer, you will need a higher value per customer to have a potential exponential business model.
When solving problems with major market potential, you are seldom alone. To be a disruptive force in the market and experience exponential growth, your offering’s value must be significantly better than your competition’s.
To have significant customer movement, you need to have a value increase (we often talk about the 10x factor) significantly better than your competition’s.
What matters is the perceived value of your offering vs your competition. However, a 10% or 20% margin of value does not cut it. You need to find your 10x value differentiator for your business model to be exponential in design.
No business will experience exponential growth without the ability to attract new customers. And the ability to do so consistently at scale and over time can only be achieved if your customer acquisition costs are low compared to the product's price.
The most exponential business models have organic or viral elements, allowing for acquisition costs that are close to zero. This differs from those businesses that have spent a lot of marketing dollars on every new customer.
You can super-charge your customer acquisition by building ambassadors, partnerships, communities, or other ecosystems into your business model. Introducing the two elements of Customer Acquisition:
The combined power of viral customer acquisition, supported by ambassadors that bring in many new customers over time, is clearly an example of a highly exponential customer acquisition model.
Customer Lifetime Value consists of two parts: the length of time the customer stays with you and the value you can generate per unit of time per customer. For a consumer brand (or B2C) to stick, you have to become part of your customer's life, a habit that builds long term lifetime value. Meanwhile, for B2B, you need to become a strategic element of your customers business model or operation to build a lasting relationship.
Ultimately, the customers that are willing to stick with you and increase their purchases over time will directly contribute to exponential growth, either as returning business or in subscription models.
The most successful exponential business models have built-in economies of scale, allowing the business model to improve its margins and drive down unit costs at scale. This creates profits and resources that will be used to improve all other value drivers.
We often see this in software-based business models, with close to 100% marginal margins. The ability to drive large unit sales without building new factories or hiring a large number of new people is inherently exponential at scale.
We have now identified the 5 core parts of business models that can improve any business model. However, when working together, they can also start a chain reaction of exponentiality.
So if you have a business that:
- Solves a problem for a large number of potential customers, and they have a high willingness to pay to get this solved,
- And your product solves perceived at least 10 times better than any competition,
- And you have an organic, low-cost customer acquisition model, supercharged with a partner ecosystem,
- And you can have your customers stick with you for a long time, growing their accounts continuously,
- And you have products of high margin, with a lean overhead with economies of scale,
Then you have the potential of building a true exponential company!
However, having the potential is only the start. Do you have the expertise and resources to execute exploiting this potential? We will later share more details on these different parts of exponential business models and introduce some metrics you can use to systematically design, evaluate and build exponential business models.
Remember, the exponential growth journey requires continuous testing, proving, and fine-tuning as you take your company to scale. Yet we believe the hard work is more than worth it.
More Exponential Thinking
From Start-up to Scale-up with New Normal Prove & Scale Model
Our mission at New Normal Group is to build exponential companies that chase the new normal of their industry. At the core of this is our Prove & Scale Model, designed to guide us systematically through the different building stages, all the way from start-up through scale-up.
Let’s take a walk through the main principles of the model to get a better idea of how it works.